<Thread>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
package com.day14;
//Thread(스레드) : 분신의 개념(멀티태스킹 수행)
//스레드 작업시 절대 중복되서 작업 하지 않음!!
class MyThread1 extends Thread{
private int num;
private String name;
public MyThread1(int num, String name){
this.num = num;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() { //스레드의 메소드
int i = 0;
while(i<num){
System.out.println(this.getName()+ " : " + name + i);
i++;
try {
sleep(100);//특정 메소드가 0.1초 만큼 쉬는 시간을 줌 //1000이 1초의 시간
//첫번째가 돌아가다 쉬는 시간에 두번째가 돌아가는 모습
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
}
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main 시작....");
MyThread1 t1 = new MyThread1(100, "첫번째 : ");
MyThread1 t2 = new MyThread1(200, "두번째 : ");
t1.start(); //스레드 호출(run()메소드 호출)
try {
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
System.out.println("main 종료...."); //main이 종료되어도 스레드는 종료될때까지 진행
}
}
|
|
==Console==

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
|
package com.day14;
class MyThread2 implements Runnable{
private int num;
private String name;
public MyThread2(int num, String name){
this.num = num;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(i<num){
System.out.println(name + " : " + i);
i++;
try {
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
}
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main 시작....");
Thread t1 = new Thread(new MyThread2(100, "첫번째"));
Thread t2 = new Thread(new MyThread2(200, "두번째"));
//실행순서는 CPU가 조정
t1.start(); //스레드 호출(run()메소드 호출)
//스레드 3개 실행(main, t1.start, t2start)
System.out.println("main 종료....");
}
}
|
|
==Console===

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
package com.day14;
import java.util.Calendar;
class TClock implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.printf("%1$tF %1$tT\n",Calendar.getInstance());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
}
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {//mainThread
//System.out.printf("%1$tF %1$tT\n",Calendar.getInstance()); //1$ f절 뒤에 것을 하나만 써서 중복 사용
Thread tc = new Thread(new TClock());
}
}
|
|
==Console==

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
package com.day14;
//스레드 우선순위
class MyThread4 extends Thread{
private String name;
public MyThread4(String name){
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 1;i<=20;i++){
System.out.println(name + " : " + i);
}
}
}
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread4 ob1 = new MyThread4("A");
MyThread4 ob2 = new MyThread4("B");
MyThread4 ob3 = new MyThread4("C");
//우선순위 종류 //확인하는 방법
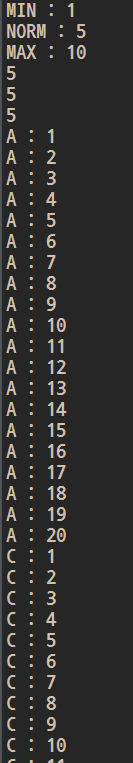
System.out.println("MIN : " + Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);//1
System.out.println("NORM : " + Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);//5 //보통 Thread의 우선순위
System.out.println("MAX : " + Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);//10
//스레드 기본 우선순위
System.out.println(ob1.getPriority());//5
System.out.println(ob2.getPriority());//5
System.out.println(ob3.getPriority());//5
//우선순위를 변경
//ob1.setPriority(1); 을 줘도 가능함(가로 안에 1~10 사이의 값으로 조정함)
ob1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);//1
ob2.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);//5
ob3.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);//10
}
}
|
|
==Console==
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
package com.day14;
//Daemon 스레드
//다른 스레드에 도움을 주는 스레드로 다른 스레드가 종료되면 데몬 스레드가 종료되지 않아도 프로세스가 종료된다.
class MyThread5 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i++){
System.out.println(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
}
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main 시작....");
//일반 스레드
Thread t1 = new Thread(new MyThread5());
Thread t2 = new Thread(new MyThread5());
Thread t3 = new Thread(new MyThread5());
//데몬 스레드 지정 //메인이 진행하는 동안만 진행함 //다른 스레드가 종료 시 데몬스레드는 강제 종료
t1.setDaemon(true); //데몬스레드의 기본은 false
t2.setDaemon(true);
t3.setDaemon(true);
try { //메인절을 1초 쉬어라
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
try {
//스레드가 종료될때까지 기다렸다가 메인절 종료
t1.join();//t1이 종료할 때까지 기다려
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
System.out.println("main 종료....");
}
}
|
|
==Console==

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
|
package com.day14;
//스레드 생명주기(Time to Live:TTL)
class MyThread6 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("스레드 시작");
System.out.println("우선 순위 : " + getPriority());
System.out.println("스레드 이름 : " + getName()); //내부적 스레드 이름은 0,t1,t2순으로 진행됨
//0.5초 쉼
sleep(500);
//우선순위 변경
setPriority(2);
System.out.println("변경된 우선순위 : " + getPriority());
System.out.println("스레드 종료....");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = Thread.currentThread(); //currentThread : main스레드
Thread t2 = new MyThread6(); //upcast
System.out.println("main스레드 우선순위 : " + t1.getPriority());
System.out.println("main스레드 이름 : " + t1.getName());
System.out.println("start()메소드 호출 전의 isAlive : " + t2.isAlive());//false(시작전이기 때문에) //생존여부 확인
//t2의 우선순위
System.out.println("t2의 우선순위 : " + t2.getPriority());
//t2의 우선순위 변경
t2.setPriority(1);
try {
//0.1초 쉼
Thread.sleep(100);
//t2종료 확인
System.out.println("t2 살아있냐? : " + t2.isAlive());
//1초 쉼
Thread.sleep(1000);
//t2종료 확인
System.out.println("1초 후 t2 살아있냐? : " + t2.isAlive());
t2.join();//main 기다려줘
System.out.println("t2 그래도 살아있냐? : " + t2.isAlive());
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
|
|
==Console==

<인터럽트>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
|
package com.day14;
//인터럽트
//우선순위가 높은 프로그램을 먼저 실행시키고, 다시 돌아온다
//세수 -> 전화 -> 택배 -> 전화 -> 세수 -> 밥 -> 교육원 //진행 하다 우선순위를 실행 후 역순으로 재진행
class MyThread7 extends Thread{
private Thread next;
public void setNext(Thread next){
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 1; i<=20; i++){
try {
sleep(2000);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
System.out.println(getName() + " : " + i);
if(next.isAlive())//아래의 setNext가로 안의 값이 살아 있는지 확인
next.interrupt(); //Thread가 살아있으면 중지시키고 다음 스레드를 진행해라.
}
}
}
public class Test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread7 t1 = new MyThread7();
MyThread7 t2 = new MyThread7();
MyThread7 t3 = new MyThread7();
t1.setNext(t2); //꼬리물기 실행
t2.setNext(t3);
t3.setNext(t1);
t1.interrupt();
}
}
|
|
==Console==

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
package com.day14;
class MyThread8 implements Runnable{
private int bank = 10000;
private int getBank(){
return bank;
}
private int drawMoney(int m){
bank -= m; //bank = bank - m;
return m;
}
@Override
public void run() {
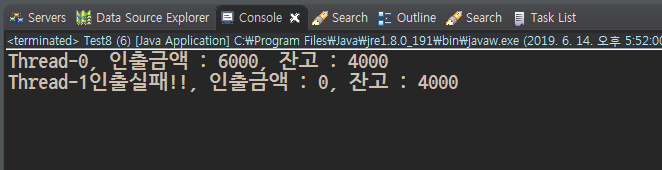
int money_need = 6000;//인출금액
int money;
String msg = "";
try {
synchronized (this) {//동기화(보호) 블럭
if(getBank()>=money_need){
Thread.yield();//yield : 첫번째 스레드가 두번째 스레드에게 양보
money = drawMoney(money_need);
}else{
money = 0;
msg = "인출실패!!";
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + msg + ", 인출금액 : " + money + ", 잔고 : " + getBank());
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
public class Test8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread8 ob = new MyThread8();
Thread t1 = new Thread(ob); //interface 사용 시 new MyTread8 대신 ob 사용
Thread t2 = new Thread(ob); //Thread는 서로 run을 점유하려고 하기 때문에 겹칠 수 있음.
}
}
|
|
==Console==
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
|
package com.day14;
class MyThread9 implements Runnable{
private int bank = 10000;
private int getBank(){
return bank;
}
private int drawMoney(int m){
if(getBank()>0){
bank -= m;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", 인출 : " + m + ", 잔액 : " + bank);
}else{
m = 0;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "잔액부족!!");
}
return m;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this) {
for(int i = 1; i<=10;i++){
if(getBank()<=0){
this.notifyAll(); //대기상태의 스레드를 시작
break;
}
drawMoney(1000);
if(getBank()==2000||getBank()==4000||getBank()==6000||getBank()==8000){
try {
wait(); //동기화 안에서 진행중인 스레드를 일시정지 시키고 다른 스레드를 움직이게 해줌
//하나의 스레드가 사용중이면 다른 스레드는 동기화 블럭에 들어올 수 없지만 wait()가 있으면 가능하다.
//stop의 의미
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}else{
notify(); //resume의 의미
}
}
}
}
}
public class Test9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread9 ob = new MyThread9();
Thread t1 = new Thread(ob);
Thread t2 = new Thread(ob);
}
}
|
|
===Console==

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
|
package com.day14;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
//정해진 시간마다 특정 작업을 하고 싶을 때
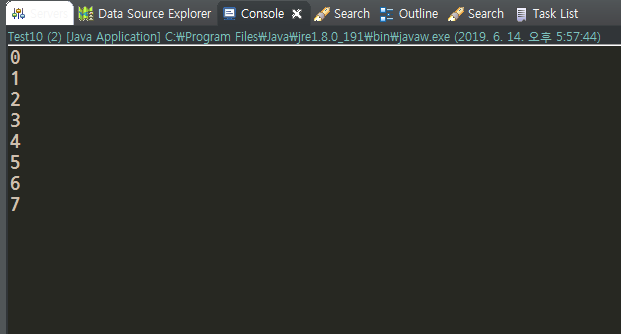
public class Test10 extends Thread {
private int num = 10;
public Test10(){
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
//무명의 클래스
@Override
public void run() {
//반복 실행할 작업
num = 0;
}
};
Timer t = new Timer(); //stopwatch의 개념
Calendar d = Calendar.getInstance();
/*
내일 0시 0분 0초부터 하루에 한번씩 반복
d.add(Calender.Date,1);
d.set(Calender.MINUTE,0); //분
d.set(Calender.SECOND,0); //초
d.set(Calender.MILLISECOND,0); //밀리세컨
t.schedule(task,d.getTime(),1000*60*60*24); //밀리세컨*초*분*시
*/
t.schedule(task, d.getTime(), 5000);
//인터벌(간격) -> 5초마다 진행
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println(num++);
try {
sleep(500);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Test10 ob = new Test10();
new Test10().start();
//객체 생성 없이(메모리 낭비 없이) 최초 1번만 시작버튼을 눌러줌
}
}
|
|
==Console==
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
package com.day14;
//스레드 그룹
//스레드를 여러개 만들어서 사용할 때 그룹지어 사용
public class Test11 {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("메인 스레드 그룹 : " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup());
System.out.println("메인 : " + Thread.currentThread());
// [main,5,main] : [name,우선순위,그룹name]
Thread t1 = new Thread(); //main threadgroup에 포함 : main, t1
System.out.println("t1 스레드 그룹 : " + Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup());
System.out.println("t1 : " + t1); //t1 = Thread.currentThread() 동일함
//[Thread-0,5,main] : [name,우선순위,그룹name]
System.out.println("--------------------------");
ThreadGroup tg = new ThreadGroup("sg"); //그룹의 이름
Thread t2 = new Thread(tg,"t2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(tg,"t3");
System.out.println("t2 : " + t2);
System.out.println("t3 : " + t3);
}
}
|
|
==Console==

'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Java Tip&Tech : 배열 복사하기 -System클래스 이용하는 방법 (0) | 2019.09.26 |
|---|---|
| Java Tip&Tech : 인터페이스와 추상클래스의 차이점 (0) | 2019.09.24 |
| Java Day13: ArrayList,Map,Generic,Excepction (0) | 2019.06.14 |
| Java Day 12 :내부클래스,Collections Framework (0) | 2019.06.14 |
| Java Day 11 : 추상 클래스, Interface (0) | 2019.06.14 |